Whole Genome Amplification (WGA) is a PCR technique that is used to produce large quantities of DNA from a small amount of starting material. Unlike conventional PCR, WGA is aimed at amplifying the entire genome of an organism rather than a specific region. The resultant amplified genomic DNA can then be used in a range of applications including KASP genotyping.
How do we do WGA?
Two main techniques exist for performing WGA:
- Primer extension pre-amplification using thermostable DNA polymerases (PEP-PCR)
- Amplification by strand displacement using Phi29 DNA polymerase.
We have evaluated both of these techniques to assess amplification efficiency, suitability of DNA for downstream applications, and cost effectiveness. We strongly favour the first technique, primer extension pre-amplification (PEP-PCR), and have developed a WGA protocol that is based on this method. This protocol employs the use of an oligonucleotide that binds throughout the genome to act as a primer, allowing replication of the genomic DNA by KlearTaq™ hot-start DNA polymerase.
We offer WGA as a service in our laboratories.
Make an enquiryRequirements and performance of WGA
A minimum mass of 50 ng DNA is required per reaction and, if the DNA is of good quality, the product is usually amplified to a concentration of 500 - 1000 times that of the starting material. This resultant DNA should be sufficient to perform KASP genotyping on at least 1000 SNPs.
If the genomic DNA is from a species with a genome size considerably larger than that of human, the required starting mass of DNA will be greater. As a guideline, divide the genome size of your organism by the size of the human genome (3000 Mbp), and use the resulting number to multiply the amount of DNA required
e.g. Triticum aestivum (wheat): 16000 Mbp.
16000 Mbp / 3000 Mbp = 5.3
You will need 5.3 times as much wheat DNA per reaction = 50 ng x 5.3 = 265 ng.
In-house validated service
We offer WGA of your DNA samples in our service laboratory. We utilise the amplification power of the Hydrocycler™ 16 that enables amplification of a large number of samples overnight. WGA reactions are performed in 96-well PCR plates (Greiner), and plates are sealed with Thermal Bond (4titude) using a Kube™ thermal plate sealer. This technique for sealing reaction plates facilitates easy access to the completed WGA reactions as the Thermal Bond seals are peelable.
WGA DNA for KASP genotyping
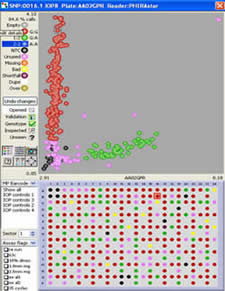
Completed WGA reactions can be used as starting template for KASP genotyping projects in our service laboratory. The figures below are the KASP genotyping results for a project within which the mass of original starting DNA was very limited. The figure on the left illustrates KASP genotyping results from the original starting material; the data points have not formed tight clusters and many of the samples have not amplified. WGA was performed in-house using 30 ng of the original DNA. The resultant amplified DNA was genotyped and results are shown in the right hand figure; the data points have formed three distinct clusters and, following checks for concordance, were found to yield 100% accuracy. The WGA reactions yielded sufficient DNA for approximately 1000 SNPs to be genotyped using KASP.
Limited DNA
Amplified DNA
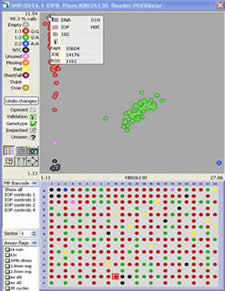
Yields
Typically, from 30 - 50 ng of genomic DNA the WGA will yield enough DNA to perform SNP genotyping on at least 1000 SNPs. In practice if the starting DNA is good it will be in excess of this. This represents an amplification of approximately 500 - 1000 fold.
Costs
The prices quoted are inclusive of a KASP genotyping chemistry reaction derived normalisation.
